Debugging Lambda Functions with Amazon Q
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that lets you run applications and services without provisioning or managing servers. It automatically handles the underlying compute resources, allowing you to focus on your code and easily scale.
In this section, you will intentionally update the data_process_action Lambda function with several bugs. Your goal is to use Amazon Q to debug and fix the issues.
Getting Started
- Open the data_process_action Lambda function in the Lambda Console.
- Click the Test button to invoke the function.
- In the test event configuration popup:
- Enter an event name like test-event.
- Use the following test event JSON to simulate an agent calling the function:
{
"agent": {
"alias": "TSTALIASID",
"name": "Agent-AWS",
"version": "DRAFT",
"id": "ADI6ICMMZZ"
},
"sessionId": "975786472213626",
"httpMethod": "GET",
"sessionAttributes": {},
"inputText": "Can you get the number of records in the databse",
"promptSessionAttributes": {},
"apiPath": "/get_num_records",
"messageVersion": "1.0",
"actionGroup": "agent_action_group"
}
- Click Test again to invoke the function.
First-Time Error
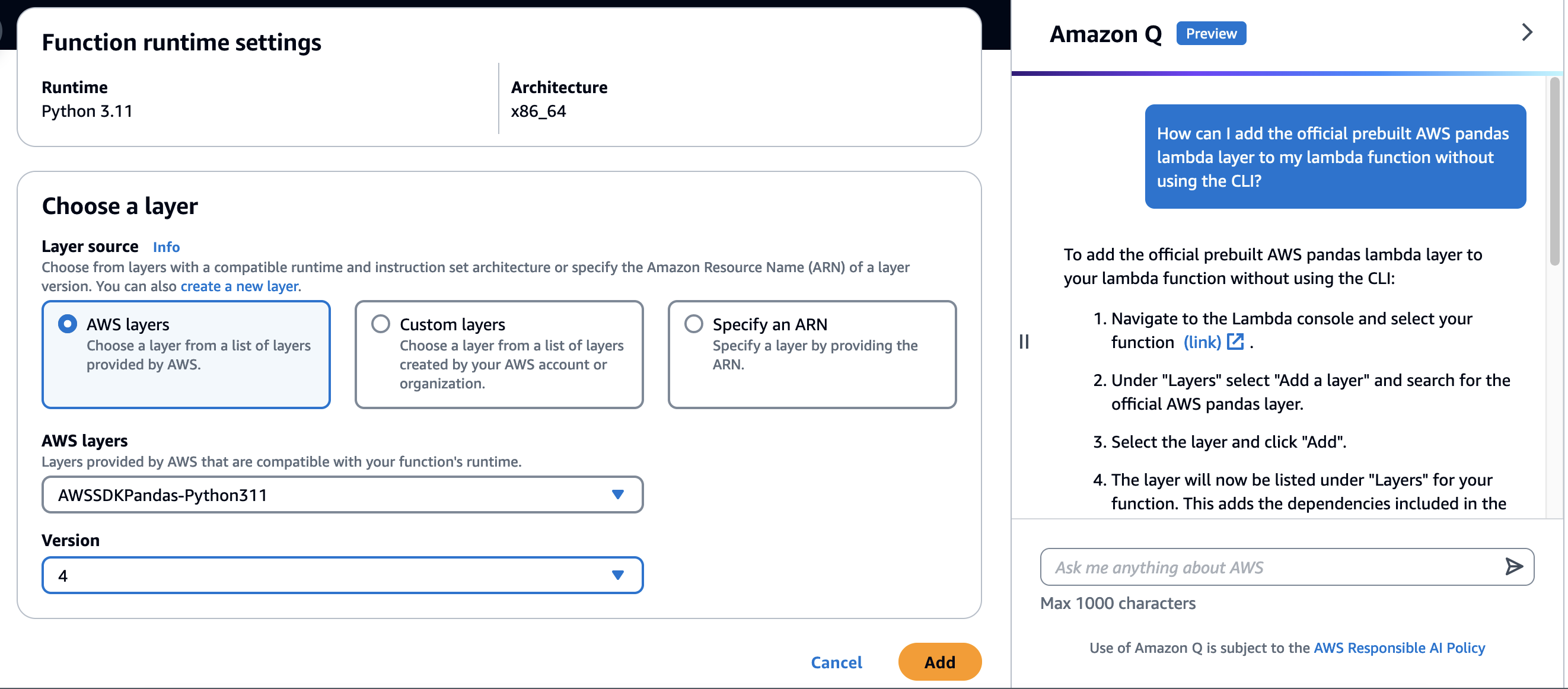
You’ll likely encounter an error because some dependencies are missing. Don’t worry, Amazon Q in the console will help you:
- Click the Q icon in the right navigation bar to chat with Amazon Q.
- Ask:
How can I add the official prebuilt AWS pandas lambda layer to my lambda function without using the CLI?
- Follow Amazon Q’s instructions to integrate the Pandas Lambda Layer.
Troubleshooting with Amazon Q
While the Amazon Q chat is helpful for general AWS questions, for more specific guidance, use the Troubleshoot with Amazon Q feature.
- In the Lambda Console, under the Test tab, run the test again by clicking Test.
- When the new error appears, click the Troubleshoot with Amazon Q button.
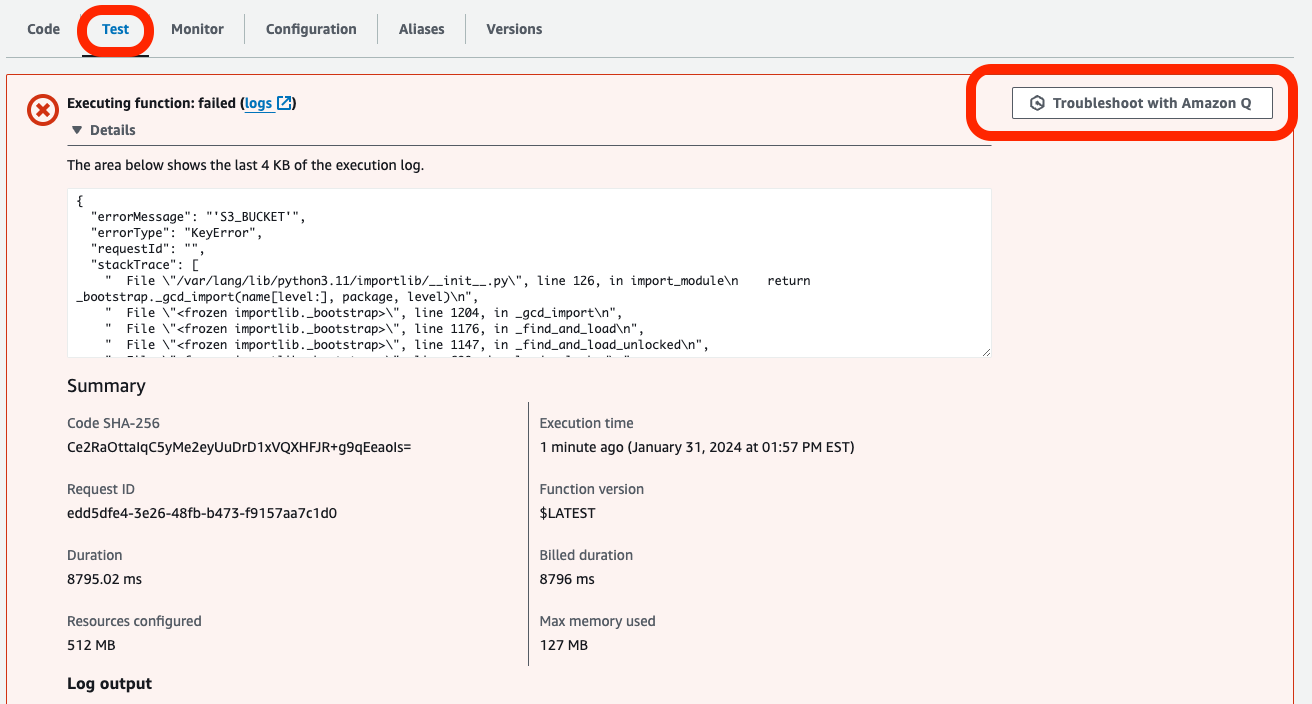
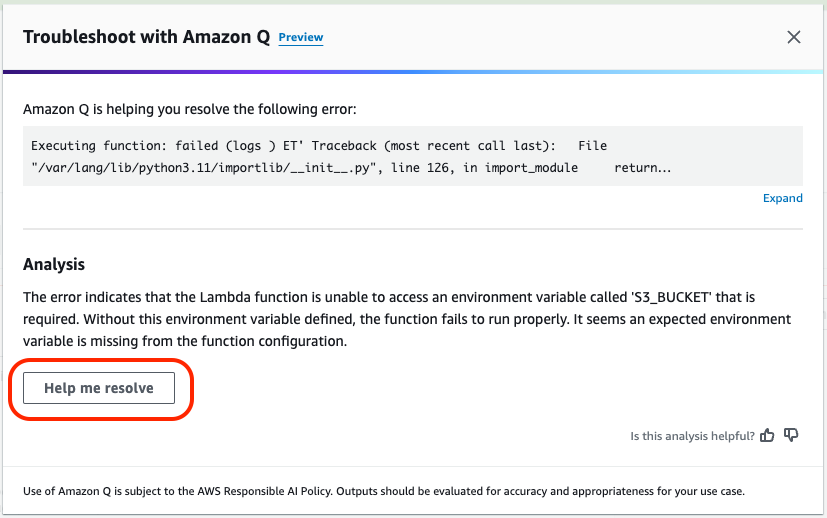
- Click Help me resolve to prompt Q for a solution.
- Follow Q’s suggestions to:
- Update the
S3_OBJECTenvironment variable if needed.- The file should be:
clickstream_data.csv
- The file should be:
- Fix other potential code issues with Q’s assistance.
- Update the
After Fixing Issues
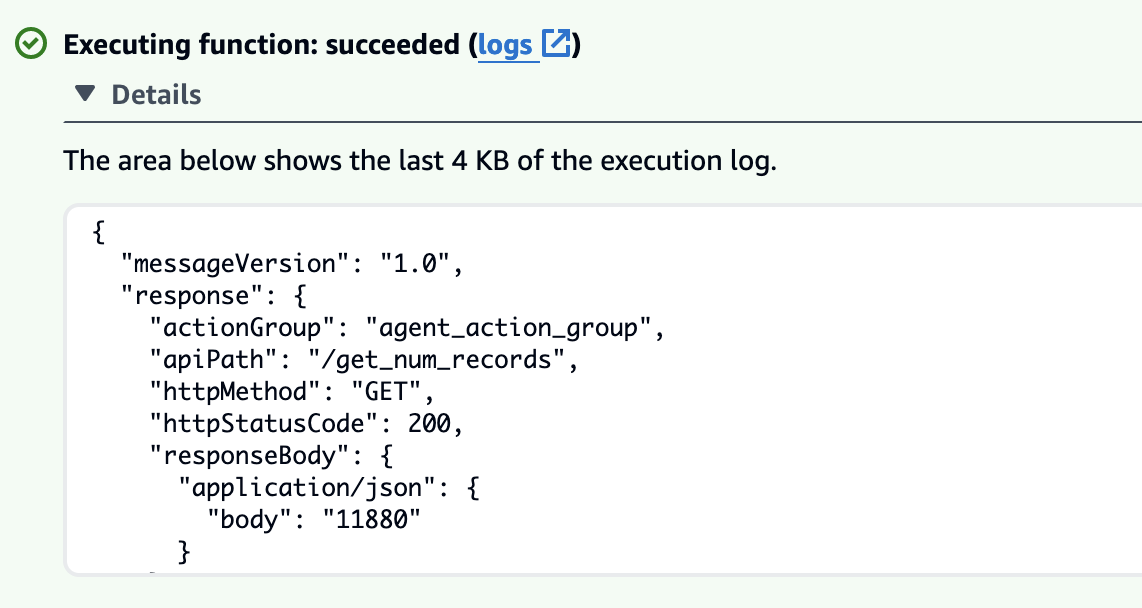
- Retest the Lambda function to confirm the errors are resolved.
- Continue using Troubleshoot with Q for each subsequent error until your Lambda runs without issues.
- A successful run will return accurate data processing results and no errors.
Need help? Here’s what to do next
- Update the S3_OBJECT Environment variable with clickstream_data.csv
- Fix the typo in the file path (replace /tmp/data,csv with /tmp/data.csv) in the Lambda function code.
- Change length to len in the Lambda function code
Here’s the full code for reference
import os
import json
import pandas
import boto3
S3_BUCKET = os.environ["S3_BUCKET"]
S3_OBJECT = os.environ["S3_OBJECT"]
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Print the received event to the logs
print("Received event: ")
print(event)
# Initialize response code to None
response_code = None
# Extract the action group, api path, and parameters from the prediction
action = event["actionGroup"]
api_path = event["apiPath"]
inputText = event["inputText"]
httpMethod = event["httpMethod"]
print(f"inputText: {inputText}")
# Check the api path to determine which tool function to call
if api_path == "/get_num_records":
s3 = boto3.client("s3")
s3.download_file(S3_BUCKET, S3_OBJECT, "/tmp/data.csv")
df = pandas.read_csv("/tmp/data.csv")
# Get count of dataframe
count = len(df)
response_body = {"application/json": {"body": str(count)}}
response_code = 200
else:
# If the api path is not recognized, return an error message
body = {"{}::{} is not a valid api, try another one.".format(action, api_path)}
response_code = 400
response_body = {"application/json": {"body": str(body)}}
# Print the response body to the logs
print(f"Response body: {response_body}")
# Create a dictionary containing the response details
action_response = {
"actionGroup": action,
"apiPath": api_path,
"httpMethod": httpMethod,
"httpStatusCode": response_code,
"responseBody": response_body,
}
# Return the list of responses as a dictionary
api_response = {"messageVersion": "1.0", "response": action_response}
return api_response
Testing the Agent
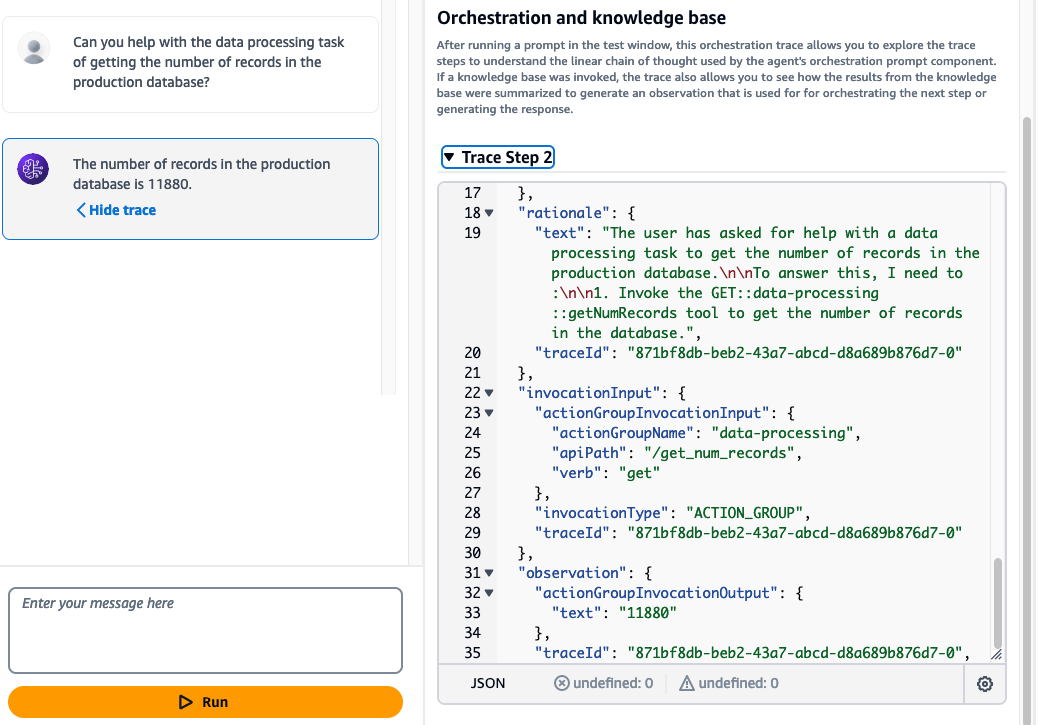
Once the Lambda function is fixed, go back to the Agent and test it again by asking:
Can you help with the data processing task of getting the number of records in the production database?
This time, the Agent will be able to provide the correct answer. You can also view the trace to see how the Agent “thought” through the process to generate the correct response.