Understanding Video with Amazon Bedrock
In this section, we’ll learn how to leverage Amazon Nova for video content analysis and understanding.
Exercise 1: Understanding Video
In this exercise, we’ll explore how to use Amazon Nova’s understanding models to analyze video content. Imagine you’re building a content management system that automatically generates engaging titles for video content. This could be useful for:
- A media company processing large volumes of videos
- A marketing team organizing video assets
- An e-learning platform cataloging educational videos
We’ll create a script that analyzes an MP4 file of the sea and uses Nova’s advanced understanding capabilities to generate creative and relevant titles based on the video’s content. This demonstrates Nova’s ability to comprehend complex visual information and generate human-like text.
Getting Started
Open the file:
video_examples/video_understanding.py
This file already contains code to ingest video and send requests to Amazon Nova. However, it is missing the correct data formatting to send the video to Amazon Bedrock.
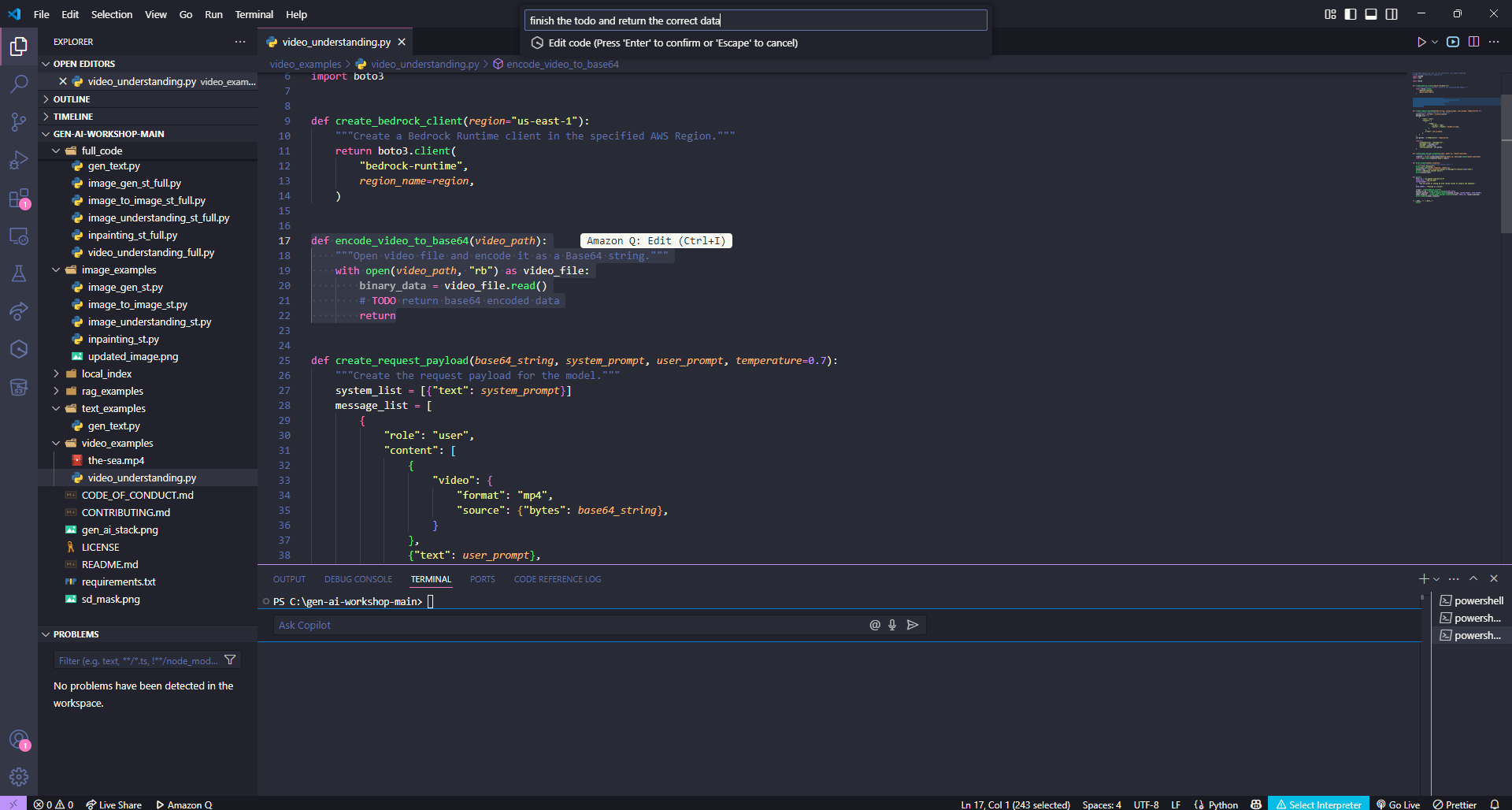
This is where you can use Amazon Q Developer to make a quick inline edit to complete the missing functionality.
Using Amazon Q Developer for Inline Editing
To complete the video formatting functionality:
- Highlight the
encode_video_to_base64function on line 17 - Press
⌘ + Ion Mac orCtrl + Ion Windows - Type the following prompt:
Finish the TODO and return the correct data
Running Your Code
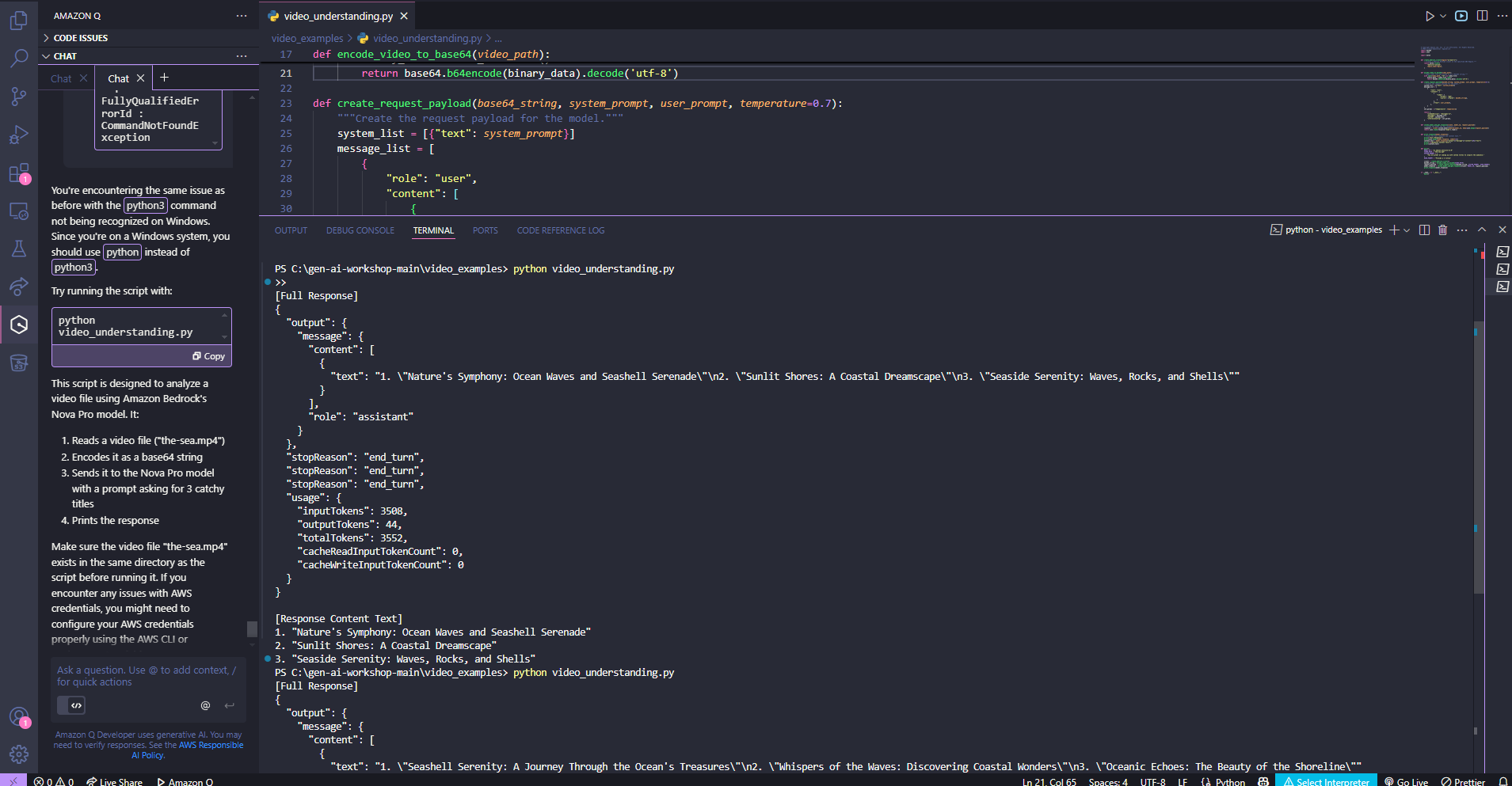
Once you’re ready to test your script:
cd video_examples
python3 video_understanding.py
If successful, you’ll see generated titles for your video.
If you encounter errors, use Amazon Q Developer to help debug the issues.
You can also reference the complete solution here:
full_code/video_understanding_full.py
Exploring Nova’s Capabilities
Once the basic implementation works, try experimenting with different prompts to explore Nova’s power:
- Generate detailed video summaries for content cataloging
- Create engaging descriptions for social media
- Produce scene-by-scene analysis for video editing
- Extract key moments or highlights for quick previews
- Generate content tags for improved searchability
These use cases show how Nova can be integrated into various content workflows and automation scenarios.
Wrap-Up
Now that you’ve gained experience using Amazon Bedrock for video understanding and text generation, we’ll move on to one of the most popular use cases in Generative AI:
Chatting with your documents ️
This next section will build on what you’ve learned and show you how to create interactive experiences with document-based content.